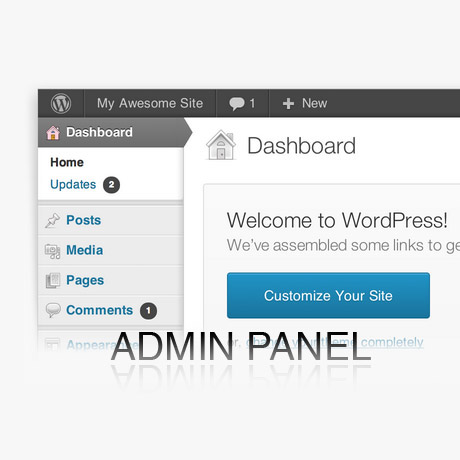
Navigating your way around in the backend area of your WordPress website need not be complicated even if you are a beginner. The WordPress Admin Panel area found in the backend is a powerful and flexible area where you can manage your website content and other WordPress functions. It has continually evolved since 2003 and with the help of and contributions from the WordPress community has improved and become more and more beautiful and user friendly.
The Administration Panel provides access to the control features of your WordPress installation. Each Administration Panel is presented in sections:
The Header
The top portion of all Panels, the header, is featured in dark shading. The header shows the name of your blog as a link to your blog’s main page, comments awaiting moderation, +New to add new posts, pages, media, or users, a Search Engines Blocked message if you Privacy settings block search engines, a favorites menu, and links to your profile (shown as your user name), and Log Out. Just below the top shaded area are two hanging tabs, Screen Options and contextual Help, that can be clicked to expand them.
The Main Navigation
On the left side of the screen is the main navigation menu detailing each of the administrative functions you can perform. Two expand/collapse arrows just below the Dashboard and Comments allow the navigation menu to collapse to a set of icons, or expand (fly-out) to show an icon and description for each major administrative function. Within each major function, such as Posts, a pull-down arrow is presented upon hovering mouse hovers over the title area. A click of that arrow expands the menu to display each of the sub-menu choices. Clicking that arrow again collapses the sub-menu.
The Work Area
The large area in the middle of the screen is the work area. It is here where specific information relating to a particular navigation choice, such as adding a new post, is presented and collected.
The Footer
Finally, in the footer, at the bottom of each Administration Panel in dark shading, are links to WordPress, Documentation, and Feedback. In addition, the version of WordPress you have installed is shown. Just below the menu tab section, if your version is NOT the latest version, you will see the message An updated version of WordPress is available. Please update now. Click on the provided link to navigate to the Updates SubPanel.
Below is a list of the submenu items you will find in your default WordPress Admin Panel main navigation menu. Some of them may or may not be included depending on the WordPress version you have installed.
Dashboard
The Dashboard tells you about recent activity both at your site and in the WordPress community at large and provide access to updating WordPress, plugins, and themes.
WordPress Updates
This sub panel gives you an easy method to update WordPress, plugins, and themes. Note not all hosts will allow the automatic update process to work successfully and will require you to manually upgrade by following the Upgrading WordPress instructions.
Posts
This sub panel is where you can publish writings, compositions, discussions, discourses, musings, and, yes, even rantings, of a blog owner and contributors. Here you can write new Posts, create new Categories, new Tags, and new Custom Fields. In addition, any Media (pictures, video, recordings, files) can be uploaded and inserted into the Posts.
Media
This sub panel allows you to upload new media to later use with posts and pages. A Flash Uploader is provided and the ability to use a Browser Uploader is supplied if the Flash Uploader does not work.
Pages
A good example of a Page is the information contained in About or Contact Pages. A Page should not be confused with the time-oriented objects called Posts, nor should a WordPress Page be confused with the word page referring to any web page or HTML document on the Web. In this Sub Panel you can select the Page to edit or delete. Multiple Pages can be selected for deletion and for editing. As with Posts, a powerful bulk edit tool allows certain fields to be edited for a whole group of Pages. A handy in-line edit tool, called Quick Edit, allows you to update many fields for an individual Page. Various search and filtering options allow you to find the Pages you want to edit or delete.
Comments/Reader Feedbacks
Comments are a feature of blogs which allow readers to respond to Posts. In this sub panel you can edit and delete as well as mark comments as spam. Comments that are awaiting moderation can be marked as approved or previously approved comments can be unapproved. Multiple comments can be selected and approved, marked as spam, unapproved, or deleted. A section at the top of the Comments SubPanel displays the number of comments awaiting moderation and the number of approved comments. A search box allows you to find specific comments.
Appearance
From the Presentation Administration Panel you can control how the content of your blog is displayed. WordPress allows you to easily style your site by either installing and activating new Themes or changing existing Themes. This sub panel includes customization controls for Themes, Widgets, Menus, Background, Header, and Theme Editor.
Plugins
Plugins allow you to add new features to your WordPress blog that don’t come standard with the default installation. This sub panel allows you to view the plugins you’ve downloaded, add new plugins, modify the plugins and choose which plugins you want activated on your site.
Users
Every WordPress site probably has at least two users: the admin, the account initially set up by WordPress, and the user account you, as the author/owner of the blog. This sub panel allows you to set up all of the user accounts you need, change user information, assign roles, or delete users.
Tools
WordPress Tools provide you the ability to speed up WordPress for your local machine, import content from other sources, export your content, or to upgrade your WordPress software to a new release. This includes the Import, Export, and Press This functions.
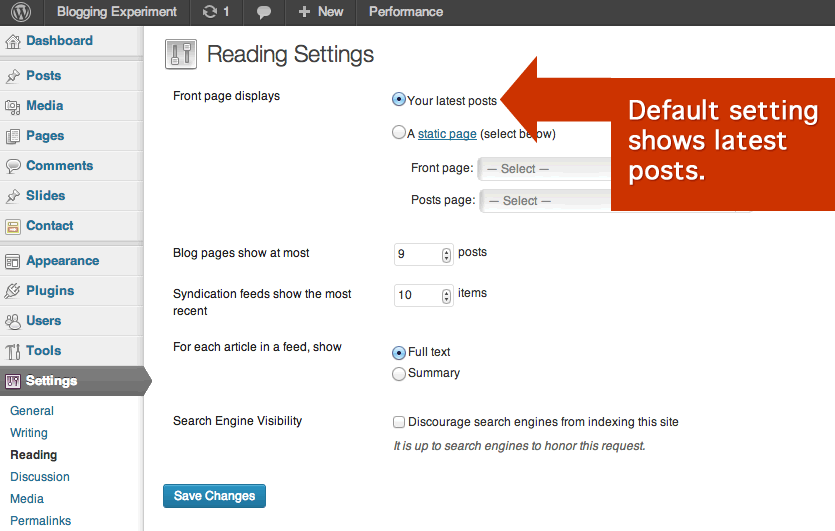
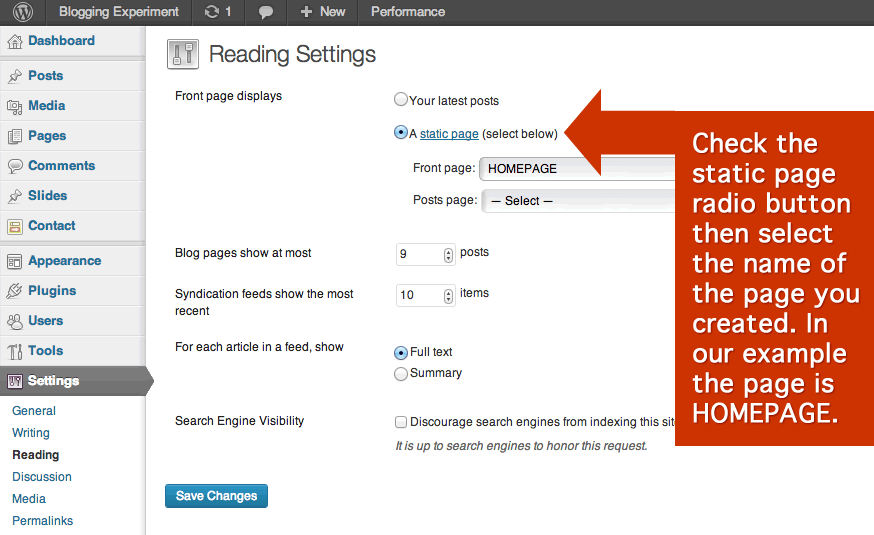
Settings
The Settings Administration Panel contains all of the settings that define your website as a whole: settings which determine how your site behaves, how you interact with your site, and how the rest of the world interacts with your site. This sub panel includes control settings for: General (basic configuration settings), Writing, Reading, Discussion, Media, Privacy, and Permalinks
(source: WordPress codex)
The backend or Admin Panel may vary from theme to theme. The look and appearance may vary depending on the customizations and tweaks done by authors and developers. Nevertheless, no matter how Admin Panel is tweaked, these basic functions are standard and generally remain the same no matter what WordPress theme you install.